Varicose Veins and Venous Diseases: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
Updated date: 8/25/2025
• Reading time: ~6 min
This text is for general information; diagnosis and treatment require an in-person medical evaluation.
Valve failure and venous dilation can cause varicose veins—visible veins, heaviness/burning, pain worsening in the evening, and swelling. Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) usually presents with sudden leg swelling, pain, warmth, and sometimes redness; due to pulmonary embolism risk, urgent assessment is required. Long-standing venous insufficiency can predispose to venous leg ulcers.
Who is more commonly affected?
- Family history, female sex, age
- Prolonged standing/sitting, inactivity
- Pregnancy, obesity
- Prior thrombosis, surgery/trauma, long-haul travel
- Certain medications and comorbidities
Key evaluation topics
- Varicose veins and chronic venous insufficiency
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and post-thrombotic syndrome
- Venous leg ulcer
- Iliac vein compression (May–Thurner) / venous outflow obstruction
- Telangiectasias (spider veins) and reticular veins
How is the diagnosis made?
In addition to the physician’s examination, the following tests may be considered in suitable patients:
- Duplex ultrasound: Assess reflux, obstruction, and venous mapping for treatment planning
- Venous mapping: Detailed evaluation of superficial and deep systems
- CT/MR venography (selected cases): Evaluate iliac/proximal stenosis or compression
- D-dimer (selected cases): Screening when DVT probability is low
Testing is guided by clinical signs, thrombosis risk, and safety criteria.
Treatment approaches
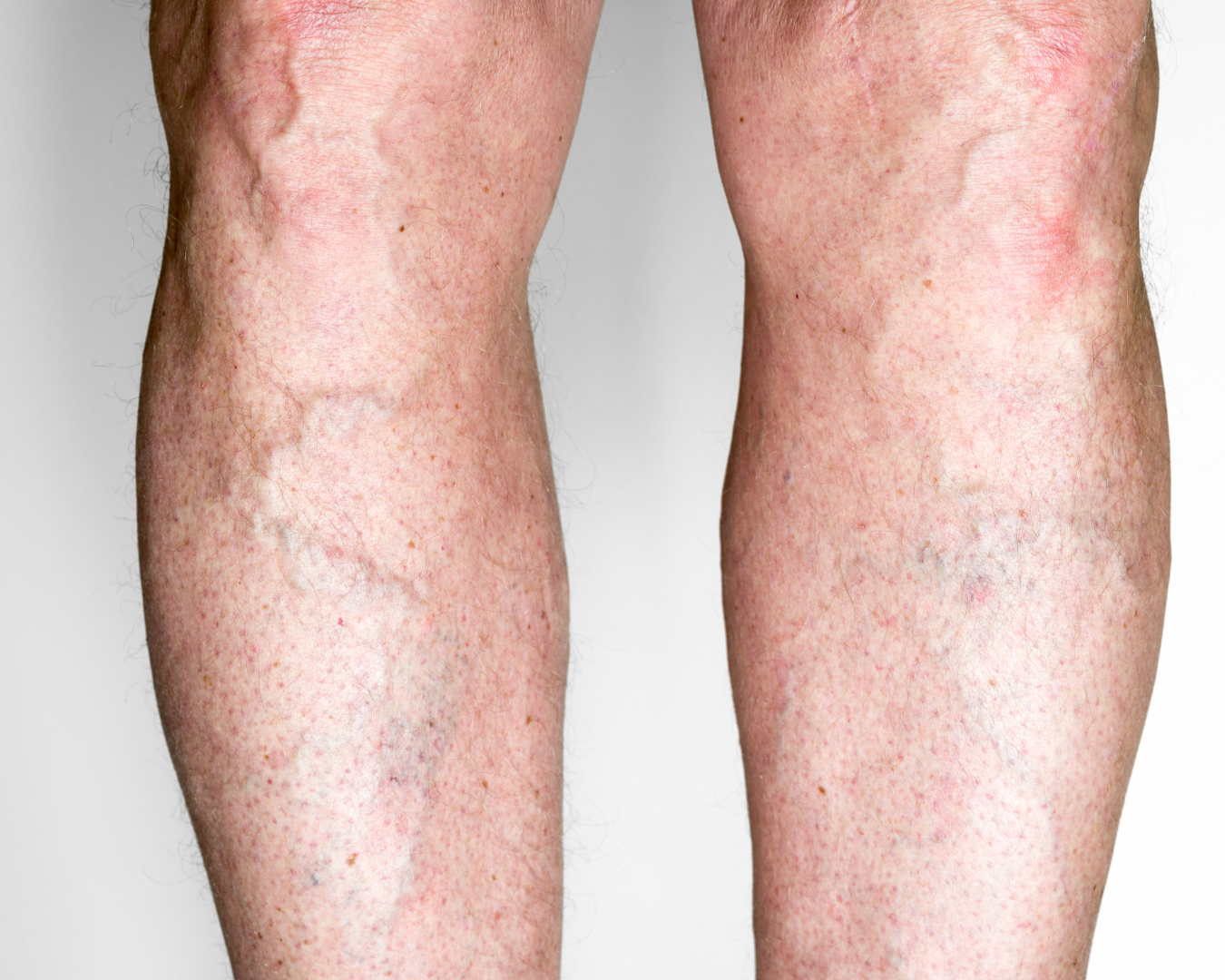
Suitability depends on venous anatomy, the location/extent of reflux or obstruction, and coexisting conditions.
1) Lifestyle and supportive care
- Compression therapy (stockings) and leg elevation
- Regular walking/exercise and weight management
- Avoid prolonged immobility; move at intervals
- Hydration and leg exercises during travel
2) Minimally invasive methods (in suitable patients)
- Endovenous thermal ablation (EVLA/RFA) or cyanoacrylate closure
- Ultrasound-guided foam sclerotherapy and ambulatory phlebectomy
- Transdermal laser for spider veins
- Anticoagulation for DVT; catheter-directed thrombolysis/thrombectomy in selected cases
- Balloon angioplasty and stenting for iliac/proximal venous stenoses
3) Surgical options (selected cases)
- Ligation of refluxing tributaries and targeted phlebectomy
- Combined/hybrid strategies in extensive reflux (as clinically assessed)
Best Practices
- Evidence-based approach: Planning aligned with current guidelines and patient safety
- Personalized plan: Targeted treatment based on duplex mapping
- Multidisciplinary collaboration: Cardiology, radiology, and hematology when needed
- Follow-up and education: Compression use, lifestyle advice, and scheduled controls
- Transparency: Clear information on options, benefits/risks, and alternatives
This page provides general information. Diagnosis and treatment require a medical examination. For appointments/contact, please use the channels on the site.
Warning and transparency
- This text is for general information.
- Images may be illustrative.

Get in touch for an expert opinion.
Contact us to receive information and book an appointment.
+90 533 357 48 68
info@zafererk.com

