Arterial Occlusive Disease & Atherosclerosis: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Approaches
Updated date: 8/25/2025
• Reading time: ~6 min
This text is for general information; diagnosis and treatment require an in-person medical evaluation.
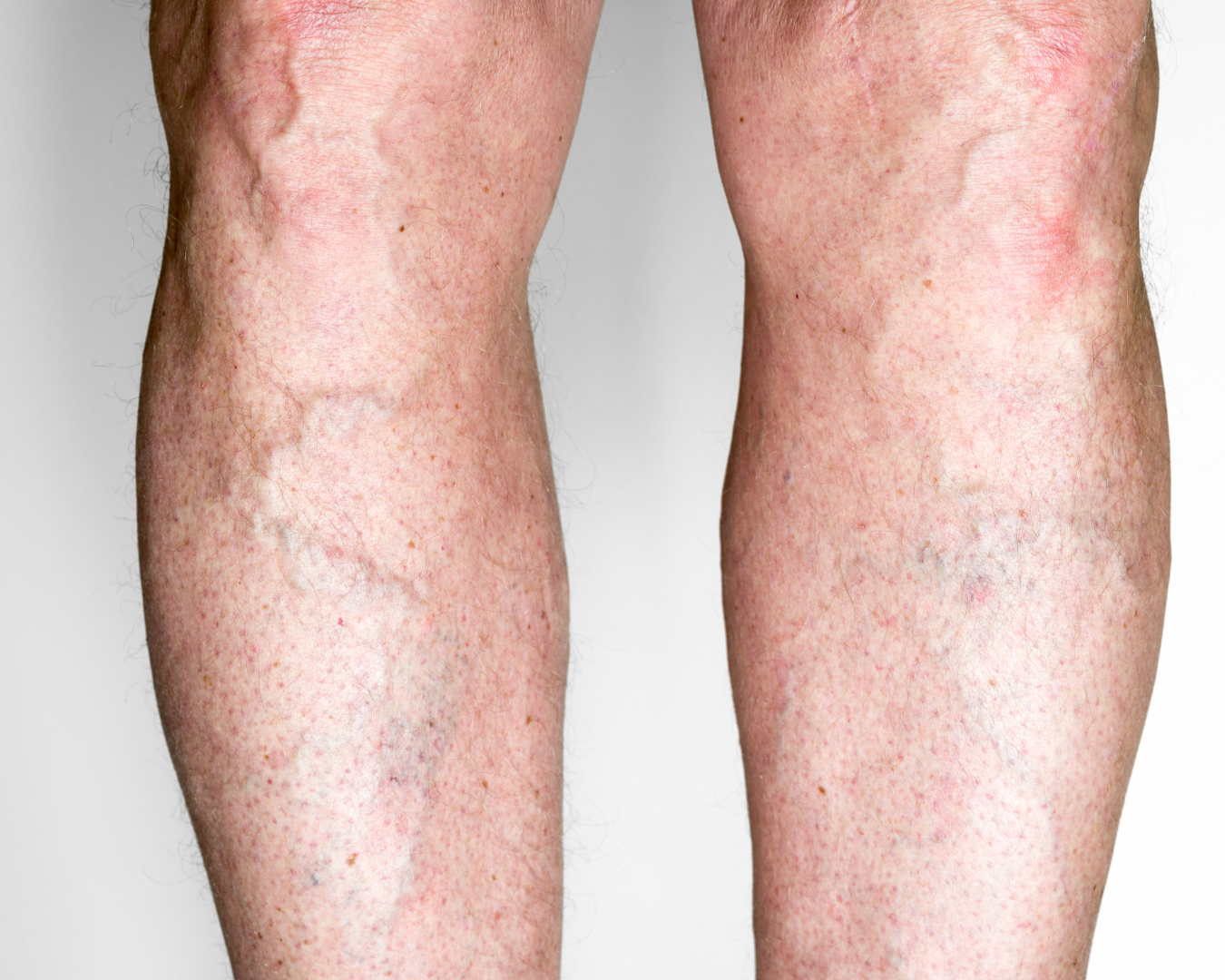
Atherosclerosis is the gradual buildup of plaque in the arterial wall that can narrow the vessel and reduce blood flow. Narrowing/blockage in the leg arteries may present with exertional pain (claudication), coldness, pallor, or non-healing wounds, while carotid (neck) artery stenosis may warn with transient speech difficulties, limb weakness, or vision loss.
Who is more commonly affected?
- Smoking/nicotine use
- Hypertension, diabetes, high LDL cholesterol
- Obesity, physical inactivity
- Older age, family history
- Chronic kidney disease
Key evaluation topics
- Lower-extremity arterial stenoses/occlusions
- Carotid artery disease
- Peripheral artery disease
- Diabetes-related stenoses/occlusions
- Other peripheral vascular stenoses/occlusions
How is the diagnosis made?
In addition to the physician’s examination, the following tests may be considered in suitable patients:
- Duplex ultrasound (Doppler): Assess flow and degree of stenosis
- Ankle–Brachial Index (ABI): Screen leg blood flow
- CT/MR angiography: Vascular mapping; may require contrast
- Digital subtraction angiography (DSA): May be combined with an endovascular procedure in the same session
Tests are selected according to clinical status, comorbidities, and safety criteria.
Treatment approaches
The choice of method is individualized based on examination, imaging findings, comorbidities, and current guidelines.
1) Lifestyle and medical management
- Smoking cessation; structured walking/exercise program
- Control of blood pressure, glucose, and cholesterol
- Nutrition counseling if needed
- Vascular-protective medications when appropriate (e.g., antiplatelets, statins)
2) Interventional methods (in suitable patients)
- Angioplasty (PTA)
- Stenting
- Other endovascular approaches as clinically appropriate
3) Surgical options (in suitable patients)
- Carotid endarterectomy (selected carotid stenoses)
- Peripheral arterial bypass/endarterectomy
- Coordinated wound care and revascularization (especially in diabetic foot)
Best Practices
- Evidence-based decision-making: Planning based on current guidelines and patient safety
- Personalized plan: Strategy tailored by examination and imaging
- Multidisciplinary collaboration: Cardiology, radiology, endocrinology when needed
- Follow-up and education: Wound care, lifestyle guidance, and scheduled controls
- Transparency: Clear information on options, potential benefits/risks, and alternatives
This page provides general information. Diagnosis and treatment require a medical examination. For appointments/contact, please use the channels on the site.
Warning and transparency
- This text is for general information.
- Images may be illustrative.
Get in touch for an expert opinion.
Contact us to receive information and book an appointment.
+90 533 357 48 68
info@zafererk.com

